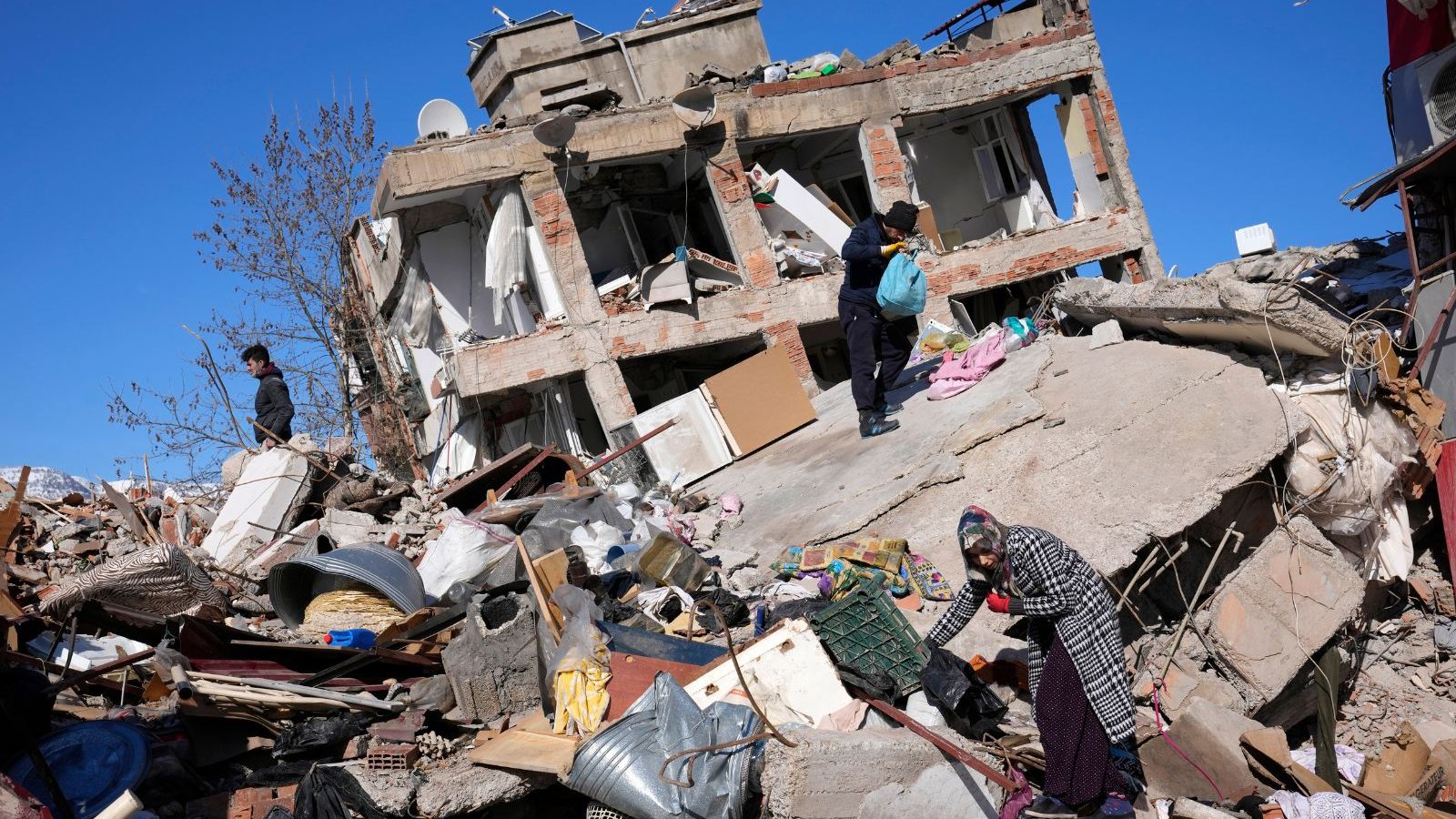
The death toll from the earthquakes in Turkey and Syria that struck on February 6, 2021 surpassed 50,000 on Friday after Turkey declared more than 44,000 people died.
More than 160,000 buildings containing 520,000 apartments collapsed or were severely damaged in Turkey, the worst in the country’s modern history, Reuters reported.
The quakes are expected to have a deep psychological impact, with children particularly vulnerable.
Apart from several consequences of a devastating earthquake, there are few concerns which seek attention of common people across the world, including in India.
Reports have shown how Turkey and Syria saw concrete structures diminishing in a few seconds. While the intensity of the earthquake was responsible for the tragic loss, local media reported there were lags in the structural issues of buildings and rules were not followed during construction.
For a country like India, which has an ambitious task to provide shelter to each and every citizen of the country, the responsibility of creating a secure real estate infrastructure becomes even more critical.
Also Read: Real Estate Frauds, Delay In Flat Possession; Check These 5 Legal Things Before Buying A House
Some of the dangers associated with earthquakes include:
The most significant danger of earthquakes is the loss of life and injuries that can occur due to collapsing buildings and other structures. In densely populated areas, the risk of casualties is even higher.
Earthquakes can cause severe damage to buildings, roads, bridges, and other critical infrastructure. This damage can result in long-term economic and social consequences.
Earthquakes can cause significant displacement of people, forcing them to leave their homes and communities. This can lead to significant social and economic disruption and can also exacerbate existing poverty and inequality.
Experts have underlined key takeaways and learnings for the industry in India.
Five takeaways for the real estate industry according to Manoj Gaur, president, CREDAI NCR and CMD Gaurs Group.
1) Unauthorised construction should be stopped as these developers do not follow the safety norms nor use adequate steel.
2) Proper construction techniques to be applied i.e. thick Column use of beams, good joints, thin slabs. In India, real estate developers who are doing construction in authorised manner take due care however developers who are doing unauthorised construction do not follow proper construction technique.
3) In India after the Gujarat incident, the government had mandated the vetting of all high rises by IIT before execution and accordingly all the drawings and construction was done.
Developers take this certification, however, proper norms are not followed in unauthorised constructions. Government shall keep proper check on unauthorised construction.
4) With various technological advancements including simulations, artificial intelligence and BIM models in place, more and more safety will be incorporated in the designs.
5) Equal focus is required in the execution of construction and adherence to structural plans is to be ensured at the development stage.
Anubhav Gupta, CEO- Vikhroli; Chief ESG, sustainability and CSR officer, Godrej Properties, also underlined key learning for the industry in the Indian context.
1. Address the aspirations of potential homeowners through information and education. Provide basic information that they should have when buying flats in multi-storey buildings.
Use information from reputable sources such as the ‘Simplified guidelines for Earthquake safety of buildings from the National Building Code of India 2016’ prepared as a collaboration between the National Disaster Management Authority and the Bureau of Indian Standards. It guides current and potential home owners towards reducing losses in future in the aftermath of the negative fallout of this natural event.
2. The industry should integrate internal check lists that ensure design and construction quality throughout the development process. These would:
A. Check if the Reinforced Concrete (RC) Frame buildings have (a) structural walls along the building height, (b) 135° hook ends in transverse ties, and (c) additional horizontal RC elements to break slender masonry infill walls into smaller panels.
B. Ensure that RC works are cured for the prescribed duration using potable water.
C. Secure heavy objects like water tanks and utilities like electricity, gas and water lines properly to RC members.
D. Ensure regular maintenance of buildings, repair of minor structural and non-structural damages, plumbing items/ water leakages from joints, electrical items, and general cleaning of roofs, balconies and ledges.
3. Ensure that the design addresses the requirements of potential earthquakes. Buildings that are symmetrical and regular in plan and elevation are considered more suitable for earthquake-resistant construction. Square or rectangular plan shaped buildings ensure the least damage during the strong earthquake ground shaking. This in no means implies that all buildings must be square.
It is however essential to understand the implications of design and take appropriate actions to counter the effects. Any shape other than a square or rectangle is expected to sustain more damage and special attention should be made to strengthen the corners by competent Structural Engineers.
4. Ensure the earthquake resistant design requirements of NBC 2016 are complied with. The cost of construction with earthquake resistant measures is marginally higher.
The additional initial cost required could typically be about 3-4% higher in residential building and 2-3% higher in office buildings. This increase is essential for incorporating earthquake resistant features in structural elements and making them robust to resist earthquake shaking. SAFETY First should be the motto.
5.Design and build Reinforced Concrete (RC) buildings that are most suitable for earthquake prone areas
Multi-storeyed RC frame buildings consist of horizontal members (beams and slabs), vertical members (Columns and Structural Walls), and masonry infill walls. During major earthquakes worldwide in the last four decades, it is observed that RC Buildings with Moment Frames (made of beams, columns and slabs) collapsed during strong earthquake ground shaking.
On the other hand, RC Buildings with Moment Frames together with RC Structural Walls have performed well with no collapse.
Buildings on stilts are unsafe in earthquake prone areas. Also, any building with little or no walls in any upper storey should not be acceptable in buildings built in earthquake prone areas.
An open storey with significantly reduced lateral stiffness and lateral strength should not acceptable in a building to be built in earthquake prone areas, irrespective of whether such a storey is located in the basement storeys, ground storey or any other storey above. Such buildings have shown consistently poor performance during past earthquakes across the world.
Read all the Latest Business News here