Early symptoms to know
The early symptoms of the disease are fatigue, fever, muscle aches, especially in the large muscle groups like the thighs, hips, back, and sometimes shoulders.
“Four to 10 days after the initial phase of illness, the late symptoms of HPS appear. These symptoms include coughing and shortness of breath. Patients might experience tightness in the chest, as the lungs fill with fluid,” the US CDC warns about the disease.
Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome is a complication associated with hantavirus infection. The symptoms of the complication develops within 1 to 2 weeks. Initial symptoms are intense headaches, back and abdominal pain, fever/ chills, nausea and blurred vision.
At a later stage the patient might develop low blood pressure, lack of blood flow (acute shock), internal bleeding (vascular leakage) and acute kidney failure.
Preventive measures
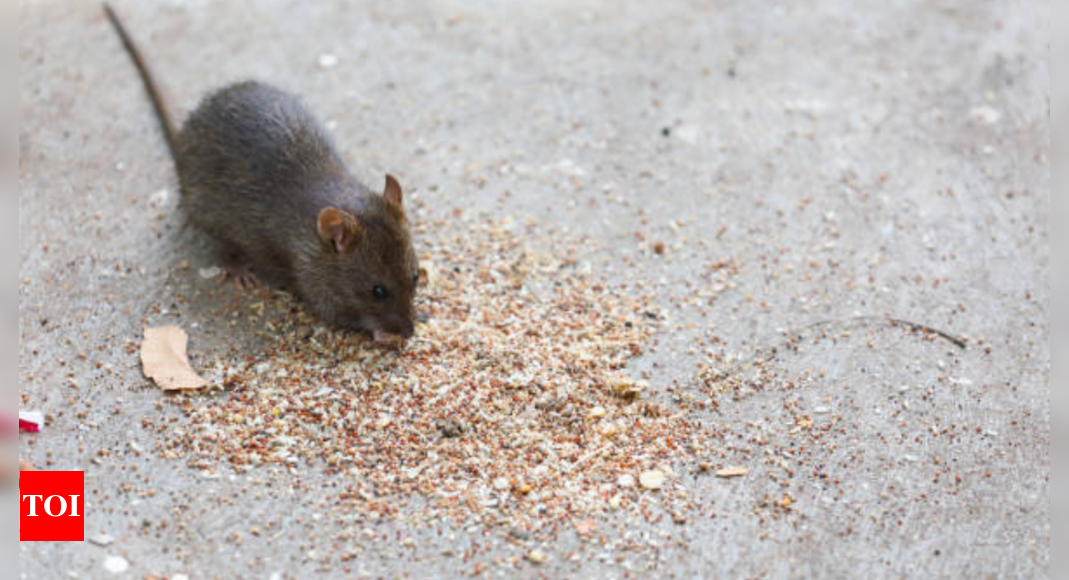
Hantavirus prevention is crucial due to the serious health risks associated with this viral infection, which can lead to hantavirus pulmonary syndrome or hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Effective prevention begins with minimizing exposure to rodents, as hantavirus is primarily transmitted through contact with rodent urine, droppings, or saliva. Ensure that homes and workplaces are kept clean and free from rodent infestations. Seal entry points such as gaps in doors, windows, and foundations to prevent rodents from entering. Use traps or professional pest control services to manage rodent populations safely.
Additionally, it is essential to use protective measures when cleaning areas contaminated with rodent droppings or urine. Wear gloves, a mask, and goggles to avoid direct contact and inhalation of dust. Moisten droppings or urine with a disinfectant before cleaning to reduce aerosolization of potentially infectious particles. Dispose of contaminated materials carefully and wash hands thoroughly afterward.
Dengue: Early signs and preventive measures to stay safe
Awareness and education are vital for effective prevention. Be cautious in outdoor settings, particularly in areas where rodents are common, such as rural or forested regions. Regularly monitor and manage rodent control practices to safeguard your health and prevent hantavirus transmission.
Hantavirus in India
As per a research study, the first hantavirus isolate to be cultured, Thottapalayam virus, is the only indigenous isolate from India, isolated from an insectivore in 1964 in Vellore, South India. “Initially believed to be an arbovirus, this isolate was later proved to be a member of the family Bunyaviridae and genus Hantavirus, based on electron microscopic and serological studies,” the researchers have said in the 2023 study.
While it is not considered a major public health concern, cases have been reported sporadically. The virus, primarily transmitted through contact with rodent droppings, urine, or saliva, poses risks in areas with rodent infestations.